Dynamics of chromatin structure and transcription regulation
Team Leader : Laszlo TORA
Department : Development and stem cells
.jpg) We are recruiting a M2 intern for the 2023-2024 academic year!
We are recruiting a M2 intern for the 2023-2024 academic year! RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcription initiation requires the stepwise assembly of protein complexes on core promoters forming the preinitiation complex (PIC), as a result of interactions with enhancers, transcription factors and transcriptional co-activators. A functional PIC is composed of Pol II and 6 multi-protein complexes called general transcription factors (GTFs): TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE, THIIF and TFIIH. TFIID is an evolutionary conserved GTF from yeast to mammals and plays a major role in transcription initiation as it is the first GTF to initiate PIC assembly by recognizing the promoter sequences. TFIID is a large multi-protein complex composed of the TATA binding protein (TBP) and 13 TBP-associated factors (TAF1-13) in metazoans.
The traditional text-book model suggesting that transcription initiation is always regulated by the same transcription complexes has been challenged in metazoans in the last decade:
- in some specific cellular contexts, Pol II transcription is unaffected by the absence of certain TAFs and even TBP, suggesting that transcription initiation might be mediated by partial TFIID complexes. In particular, mutations in TAF1, TAF2, TAF4, TAF6, TAF8 and TAF13 have been identified in human patients with neurodevelopmental disorders (ND) and intellectual deficiencies, forming a new class of NDs called "TAFopathies".
- Several TAFs have paralogs, some of which are associated with specific cell lineages, suggesting that there are in fact several TFIIDs complexes
- three metazoan TBP homologues were identified on the basis of their conservation of the characteristic C-terminal DNA-binding domain that could form TFIID-like complexes. We have recently shown that during oocyte growth, TFIID is not present, being replaced by an oocyte-specific TBPL2/TFIIA complex.
Our projects focus on studying the variability and functionality of these different transcription initiation machineries during differentiation but also in pathological conditions.
- What is the nature and variability of the protein complexes associated with Pol II transcription initiation?
- How does this variability, under normal conditions or in human pathologies, influence Pol II-mediated gene expression?
Team Leader : Laszlo TORA
Department : Development and stem cells
Axis 1: Transitions in transcription initiation machinery from oocyte growth to zygotic genome activation
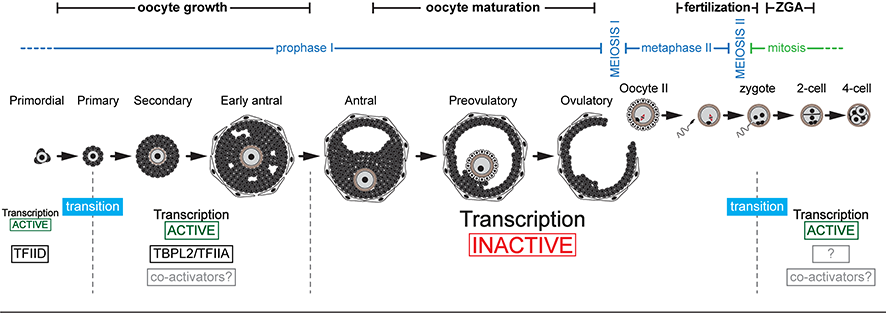
Between the end of gametogenesis and the beginning of embryonic development, there are two transcriptional context transitions:
- the initiation of transcription during oocyte growth is mediated by the TBPL2/TFIIA complex instead of TFIID allowing the establishment of the maternal transcriptome.
- At the end of oocyte growth, transcription stops. The steps of oocyte maturation, fertilization and early development are therefore controlled by the regulation of the stability and translatability of the maternal transcriptome. Transcription does not resume until before the first division, at the time of zygotic genome activation (ZGA). The nature of the protein complexes involved in the initiation of transcription during this second transition is not known.
Axis 2: Pathologies associated with variability within the protein complexes associated with transcription initiation
Our aim is to better understand the functionality of the complexes involved in transcription initiation by generating mutations or by studying mutations associated with pathologies such as TAFopathies.
- What can we learn about the mechanisms of transcription initiation from mutations in transcription complexes?
- What can we learn about molecular pathological mechanisms?
Our models:
- patient’s cells
- mouse models replicating the mutations identified in patients to study the effects at a whole organism scale and to derive embryonic stem cells and differentiate them into neural progenitors and neurons for molecular studies
- in the long term, we want to reproduce the mutations in hiPSCs (human induced pluripotent stem cells) to study the molecular effects in differentiated cells (2D or organoids)
Biomedicines ; Volume: 10 ; Page: 2647
Nucleic Acids Research ; Page: gkac637
International Journal of Molecular Sciences ; Volume: 23 ; Page: 7459
Biochemical Society Transactions ; Volume: 49 ; Page: 2051-2062
Cell Death and Differentiation ; Volume: 28 ; Page: 2385-2403
Nature Communications ; Volume: 11 ; Page: 6439
Nature Communications ; Volume: 11 ; Page: 6439
Cell Reports ; Volume: 29 ; Page: 1410-1418.e6
Nature Communications ; Volume: 10