Pathophysiological role of nuclear receptor signalling
Team Leader : Daniel METZGER
Department : Functional genomics and cancer
SUBGROUP LEADER
Androgens increase muscle mass, but their therapeutic efficacy in sarcopenia is limited due to their effects on prostate cells. Conversely, long-term treatments with anti-androgens have numerous side effects, including muscle wasting. The latter is also observed with glucocorticoid treatments (e.g. prednisone, dexamethasone), the most commonly prescribed drugs for chronic inflammatory disorders, such as asthma and arthritis. Interestingly, androgen and glucocorticoid receptors recognize similar DNA sequences.
Our project aims to understand the mechanisms underlying the action of these hormones to reduce their side effects on skeletal muscles via two approaches: (i) identifying the molecular determinants that confer androgen- and glucocorticoid- tissue specificity, and (ii) modulating the activity of epigenetic coregulators, including the histone demethylase Lsd1.
Team Leader : Daniel METZGER
Department : Functional genomics and cancer
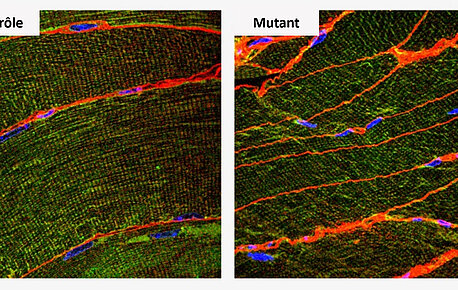
Androgens are steroid hormones that affect muscle structure and strength whose action is mediated by the androgen receptor. In a study published in…
Read more
Article in a journal
Nucleic Acids Research ; Volume: 53
Article in a journal
AJP - Endocrinology and Metabolism ; Volume: 328 ; Page: E645 - E651
Article in a journal » Data paper
Nature Communications ; Volume: 15 ; Page: 3563
Article in a journal
Frontiers in Nutrition ; Volume: 11
Article in a journal
Nutrients ; Volume: 16
Article in a journal
Steroids ; Volume: 199 ; Page: 109306
Article in a journal
Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE ; Volume: 197 ; Page: 1-21
Article in a journal
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle ; Volume: 14 ; Page: 1707 - 1720
Article in a journal
Nucleic Acids Research ; Volume: 49 ; Page: 4472 - 4492
Article in a journal
Cell Death and Disease ; Volume: 8