Differentiation and physiopathology of endocrine cells in the pancreas and intestine
Differentiation and physiopathology of endocrine cells in the pancreas and intestine
Our main goal is to decipher the transcriptional networks controlling the differentiation, function and maintenance of endocrine cells in the pancreas and intestine in normal and pathological conditions.
Future strategies for cell replacement therapies and regenerative medicine strongly depend on our knowledge of the detailed mechanisms that control the differentiation of multipotent stem cells into highly specialized cells. Along these lines of research, our goal is to understand how the diversity of pancreatic and intestinal endocrine cells is generated from stem/progenitor cells during embryogenesis towards adult life.
Pancreatic endocrine cells are clustered in islets embedded in the exocrine tissue. Islets contain five hormone producing cell-types, including insulin-secreting beta cells, which, in concert, control glucose homeostasis. Absolute or relative insulin-deficiency lead to diabetes. Intestinal endocrine cells, also called enteroendocrine cells (EECs), are very closely related to pancreatic islet cells with respect to their embryonic origin, differentiation programs and physiological roles in the control of energy homeostasis. EECs are rare cells found along the intestinal mucosa, they sense nutrients in the gut lumen and, in response, secrete a variety of hormones that act locally or at distance to regulate energy homeostasis via their control of intestinal absorption, food intake and insulin secretion. We showed previously that pancreatic and intestinal endocrine cells arise from progenitor cells expressing the pro-endocrine transcription factor Neurog3. In absence of Neurog3, islet cells and EECs do not form leading to neonatal diabetes and intestinal malabsorption in mice and human. Despite the identification of a few targets of Neurog3, the molecular mechanisms implementing Neurog3 endocrinogenic function are poorly understood.
We focus on the identification and study of novel effectors controlling endocrine sub-type specification and functional maturation. To tackle these questions, we use stem cell based human organoid culture systems and mouse models combined with gene editing and multi-omics approaches. We hope that our studies will contribute to the development of a cell-based therapy in diabetes, as well as to understand the mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of islet and enteroendocrine hormone failures in human.
.png)
Members
Researchers
PhD students
Technicians
Funding and partners
The team was supported by founding from
- Novonordisk Foundation
- Agence National pour la Recherche (ANR)
- Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM)
- Novonordisk
- National Institute for Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease (NIDDK)
- Société Française des Diabétiques (SFD)
- Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (JDRF)
- European Union (6th FP)
- Institut Benjamin Delessert
- Association Française des Diabétiques (AFD)
- Université de Strasbourg
- ARC
- INSERM-AVENIR
News
FateCompass: to identify and predict the decisive criteria of cell fate
Cell differentiation is a process regulated by gene expression through the action of transcription factors. Different transcription factors and…
Read more
Resources
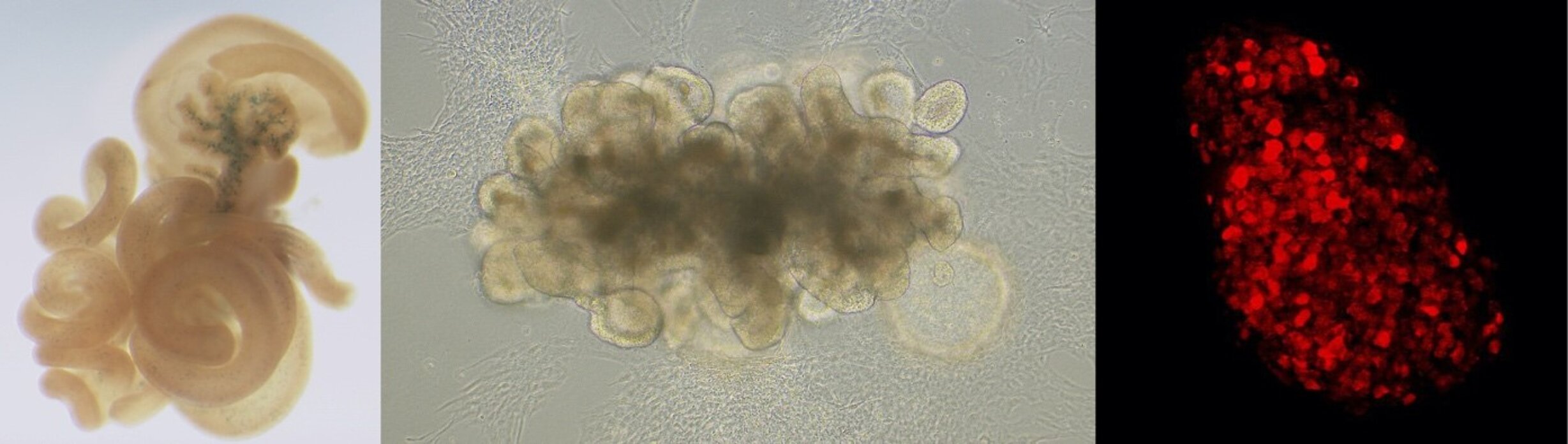
Human intestinal organoid. Enteroendocrine progenitors are expressing the transcription factor NEUROG3 (red).
https://seafile.igbmc.fr/f/80de9329f382470d80de/?dl=1
Publications
2025
Article in a journal
Extracellular matrix-driven metabolic control of pancreatic endocrine lineage allocation
- Christine Ebeid
- Adam Rump
- Chenglei Tian
- Anant Mamidi
- Adèle de Arcangelis
- Gérard Gradwohl
- Henrik Semb
EMBO Reports ; Page: Online ahead of print
Article in a journal
Unraveling enteroendocrine cell lineage dynamics and associated gene regulatory networks during intestinal development
- Sara Jiménez
- Florence Blot
- Aline Meunier
- Rishabh Kapoor
- Valérie Schreiber
- Colette Giethlen
- Sabitri Ghimire
- Maxime Mahe
- Nacho Molina
- Adèle de Arcangelis
- Gérard Gradwohl
Biology Open ; Volume: 14 ; Page: bio062083
2023
Article in a journal
An Efficient Protocol for CUT&RUN Analysis of FACS-Isolated Mouse Satellite Cells
- Kamar Ghaibour
- Joe Rizk
- Claudine Ebel
- Tao Ye
- Muriel Philipps
- Valérie Schreiber
- Daniel Metzger
- Delphine Duteil
Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE ; Volume: 197 ; Page: 1-21
Article in a journal » Data paper
Characterization of cell-fate decision landscapes by estimating transcription factor dynamics
- Sara Jiménez
- Valérie Schreiber
- Reuben Mercier
- Gérard Gradwohl
- Nacho Molina
Cell Reports Methods ; Page: 100512
Article in a journal
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 9 mediates early protection against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by regulating type I IFN production
- Shyamala Thirunavukkarasu
- Mushtaq Ahmed
- Bruce A Rosa
- Mark Boothby
- Sung Hoon Cho
- Javier Rangel-Moreno
- Stanley K Mbandi
- Valérie Schreiber
- Ananya Gupta
- Joaquin Zuniga
- Makedonka Mitreva
- Deepak Kaushal
- Thomas J Scriba
- Shabaana A Khader
The Journal of clinical investigation ; Volume: 133
Article in a journal
De la biologie du développement à la thérapie cellulaire du diabète
- Valérie Schreiber
- Gérard Gradwohl
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques
Article in a journal
Gut microbiota remodeling and intestinal adaptation to lipid malabsorption after enteroendocrine cell loss in adult mice
- Florence Blot
- Justine Marchix
- Miriam Ejarque
- Sara Jimenez
- Aline Meunier
- Céline Keime
- Camille Trottier
- Mikaël Croyal
- Céline Lapp
- Maxime Mahe
- Adèle de Arcangelis
- Gérard Gradwohl
Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology
2021
Article in a journal
The laminin-binding integrins regulate nuclear factor kappaB-dependent epithelial cell polarity and inflammation
- Eugenia M. Yazlovitskaya
- Erin Plosa
- Fabian Bock
- Olga M. Viquez
- Glenda Mernaugh
- Leslie S. Gewin
- Adele de Arcangelis
- Elisabeth Georges-Labouesse
- Arnoud Sonnenberg
- Timothy S. Blackwell
- Ambra Pozzi
- Roy Zent
Journal of Cell Science ; Volume: 134
Article in a journal
Extensive NEUROG3 occupancy in the human pancreatic endocrine gene regulatory network
- Valérie Schreiber
- Reuben Mercier
- Sara Jiménez
- Tao Ye
- Emmanuel García-Sánchez
- Annabelle Klein
- Aline Meunier
- Sabitri Ghimire
- Catherine Birck
- Bernard Jost
- Kristian Honnens de Lichtenberg
- Christian Honoré
- Palle Serup
- Gérard Gradwohl
Molecular metabolism ; Volume: 53 ; Page: 101313
Article in a journal
Adhesion receptor ADGRG2/GPR64 is in the GI-tract selectively expressed in mature intestinal tuft cells
- Kaare V. Grunddal
- Sarah Tonack
- Kristoffer L. Egerod
- Jonanthan James Thompson
- Natalia Petersen
- Maja S. Engelstoft
- Constance Vagne
- Céline Keime
- Gerard Gradwohl
- Stefan Offermanns
- Thue W. Schwartz
Molecular metabolism ; Volume: 51

