Brain development and physiology
Brain development and physiology
.png)
Whereas vitamin A is best known for its critical role during embryonic development and visual cycle (documented by 3 Nobel prizes), its post-natal activities, including in neuroprotection, modulation of neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity only start being discovered and understood. Our goal is to decipher the highly diverse functions of vitamin A, its active derivatives (retinoic acids), and the corresponding nuclear receptors (RARs/RXRs), in neural development, aging, and in stem cell control. Our studies of specific retinoid receptors and bioactive metabolites in control of diverse biological processes should contribute to a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying development and function of specific cell types and relevant neural circuits. We also investigate the therapeutic potential of specific retinoids in neurological and psychiatric diseases.
To address these questions, we use genetic, pharmacological or behavioral mouse models of specific diseases, as well as CRISPR- and viral-based approaches to control gene expression. Our mechanistic studies are guided by combination of genomic, proteomic and metabolomic data from clinics and mouse models. In collaboration with experts in chemistry we also develop new tools to study biological processes in vivo (e.g. click chemistry, novel RXR agonists). We have shown that fine-tuning of retinoic acid activity depends on its spatiotemporal patterns of synthesis (by retinol and retinaldehyde dehydrogenases) and catabolism (by CYP26 enzymes).
Our current focus relates to the role of retinoids in brain physiology and pathology, with a particular interest in basal ganglia and dopaminergic signaling, whose dysfunctions are associated with several neuropsychiatric disorders. These studies take advantage of murine models relevant to neurodevelopmental disorders, Parkinson and Huntington diseases, and depression. We also investigate mechanisms of glial cell development and biology to elaborate regenerative medicine approaches in multiple sclerosis. A long-term goal is to understand the mechanisms underlying these disorders, and develop new strategies or compounds for their prevention or therapy.

The team is composed of 3 permanent members (Research Director, Associate Prof. at Medical School, Research Engineer) and consistently hosts several PhD students & post-doc(s), as well as short-term members/interns of various horizons, including undergraduate students from University of Strasbourg, MD/PhD program, IMCBio awardees & other foreing students, thus counting on average 8-10 members.
Links to full Publication records of Wojciech Krezel: orcid.org/0000-0003-1605-3185 ; Pascal Dollé: orcid.org/0000-0002-9294-9090

Members
Researchers
Post-doctoral fellows
PhD students
Engineers
Former members
Vito Antonio Baldassarro (Post-doc ; now Assistant Professor at University of Bologna)
Agnès Bloch-Zupan (Professor at Dental Surgery Faculty, Strasbourg)
Guillaume Etter (PhD student; now Research Associate at Ste-Justine Research Centre, Québec)
Isabelle Le Roux (Post-doc, then CR CNRS; now at ICM, Paris)
Karen Niederreither (Post-doc; then Associate Professor at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and UT Austin)
Marie Paschaki (Post-doc; now Associate Professor at Lyon University)
Muriel Rhinn (CR CNRS; now in Bill Keyes' team, IGBMC)
Vanessa Ribes (PhD student; now DR Inserm at Jacques Monod Institute, Paris)
Raymond Romand (Visiting Professor from Clermont-Ferrand University)
Brigitte Schuhbaur (Research Engineer)
Julien Vermot (PhD student; now DR Inserm and Team leader at Imperial College London)
Alumni PhD students: Marta Wietrich, Agnieszka Krzyzosiak, Jabier Gallego-Llamas, Monika Rataj-Baniowska, Virginie Laugel, Carole Haushalter, Supawich Morkmued, Anna Podlesny, Marion Ciancia, Lucile Cathiard, Joanna Sobska
Our two latest graduates (PhD obtained in Dec. 2023) are Alexia Kindler & Nicolas Zinter
Alumni Post-Docs: Laura Cammas, Anna Niewiadomska-Cimicka, Mohammad Rima, Karim Matmat
Current projects
Role of retinoids in development and pathophysiology of the dopaminergic system
Even subtle alterations in dopaminergic signaling may affect brain functions, and may underlie various neuropsychiatric diseases. Our ongoing projects are focused on development and functions of the dopaminergic system in basal ganglia including striatum, a brain region important for control of motor, affective and cognitive functions. The goal is to understand how discrete developmental events contribute to physiological diversity in cognitive performance, or affective susceptibility to stress, and understand the neurodevelopmental basis of neurologic diseases. We are also testing known and newly characterized retinoids for treatment of such brain disorders in relevant animal models.
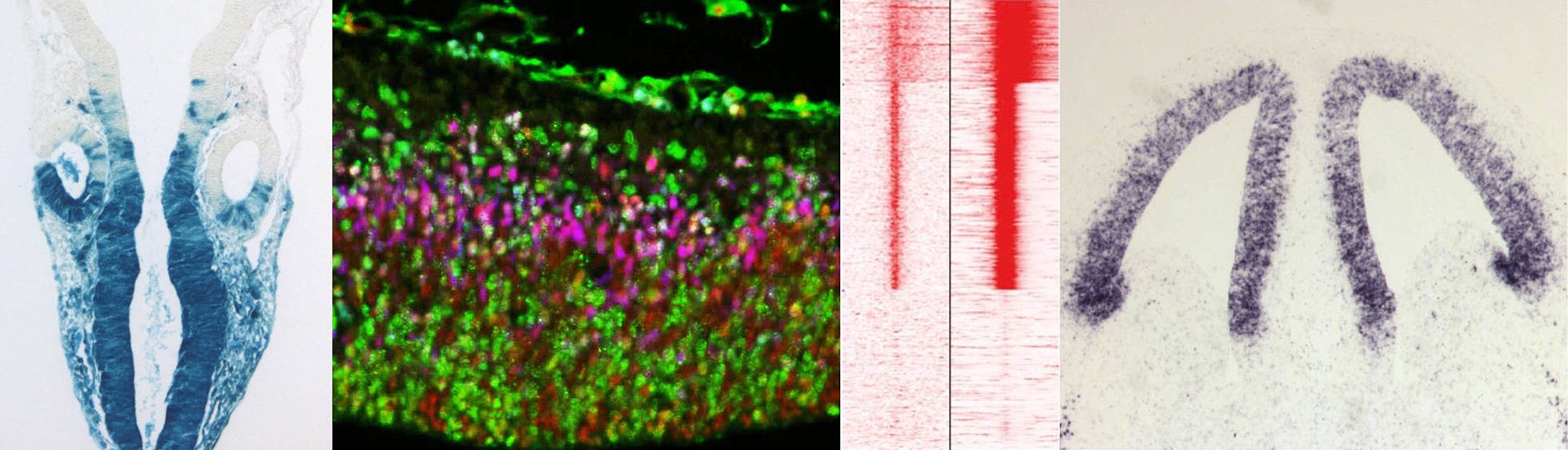
 Cell fate analyses in mouse brain : an engineered reporter gene, inserted in the mouse genome, allows lineage analysis of cells expressing a gene of interest
Cell fate analyses in mouse brain : an engineered reporter gene, inserted in the mouse genome, allows lineage analysis of cells expressing a gene of interest
Retinoids in neurodegenerative diseases
Recent data point to beneficial effects of specific retinoids or retinoid receptors in distinct neurodegenerative diseases. We investigate mechanisms underlying such activities, focusing for example on control of mitochondrial functions and calcium signaling in rare neurodegenerative diseases including Huntington disease or MCOPS12 (microphtalmia, syndromic 12 - a rare disease for which causative mutations in RAR beta have been identified), or cell differentiation and neuroinflammation in the context of regenerative medicine in multiple sclerosis. Such studies are guided by genomic and epigenetic analyses of existing and new genetic mouse models relevant for those diseases. We have also invested in innovative techniques applied to these mouse models to obtain single cell resolution in our studies.
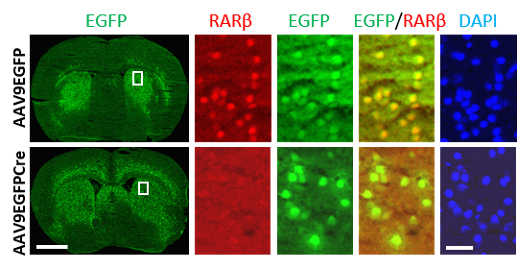 Virus-mediated deletion of RAR beta in adult mouse striatum : lower panels show absence of RAR beta protein in striatal cells, whereas a reporter EGFP gene allows to identify cells in which the corresponding locus remains active (From Ciancia et al., 2022)
Virus-mediated deletion of RAR beta in adult mouse striatum : lower panels show absence of RAR beta protein in striatal cells, whereas a reporter EGFP gene allows to identify cells in which the corresponding locus remains active (From Ciancia et al., 2022)
New tools for studies of biological processes and drug development
A recurrent challenge in modern biology is to integrate into a more global picture molecular, cellular and functional determinants of a given biological process. In collaboration with experts in synthetic, analytical and biological chemistry, we elaborate tools for multilevel studies of small bioactive molecules or circulating drugs in living organisms. The key to such approaches are rapid and irreversible chemical reactions ("click chemistry"), which can be carried out in a complex biological environment. A prototypic example is the development of click chemistry reactions in the living organism, which we showed useful for rapid inactivation and renal elimination of a purpose-designed drug. This work paves the way for new strategies in drug design and studying of endogenous metabolic or signalling processes.
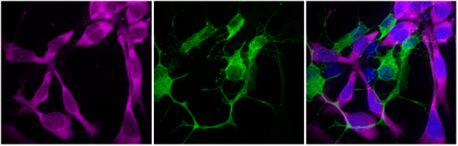 An example of cell-type specific chemoprobe reaction
An example of cell-type specific chemoprobe reaction
Collaborations and networks
Collaborators (in alphabetic order):
Vito Antonio BALDASSARRO (ORCID ID: 0000-0003-1020-4261) and Laura CALZA (ORCID ID: 0000-0002-4426-8477), Department of Veterinary Medical Science, Department of Pharmacy and BioTechnology, University of Bologna, Italy) – Multiple sclerosis, glial cell biology, endocrinology
François FENAILLE, ORCID ID: 0000-0001-6787-4149 , CEA, Frédéric Joliot Institute for Life Sciences, Paris, France – Analytical chemistry
Emmanuel HAFFEN, ORCID ID: 0000-0002-4091-518X, CHU de Besançon, Université de Franche-Comté, Laboratoire de recherche Intégrative en Neuroscience & Psychologie Cognitive, Besançon, France – Psychiatry, clinical and experimental neurobiology
Angel de LERA, ORCID ID: 0000-0001-6896-9078, Universidade de Vigo, Vigo, Galicia, Spain – Chemistry of retinoids
Jacques MICHAUD, ORCID ID 0000-0002-9912-0293, CHU Sainte-Justine Research Center, Department of Pediatrics, Department of Neurosciences, Université de Montréal, Québec, Canada – Clinical and experimental studies of neurodevelopmental diseases, rare diseases
Shin-Ichi MURAMATSU, ORCID ID: 0000-0002-3185-7790, Jichi Medical University, The Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo – Gene therapy using viral vectors, dopamine signaling, Parkinson disease
Olivier POCH, ORCID ID: 0000-0002-7134-3217, Complex Systems and Translational Bioinformatics, iCUBE, University of Strasbourg, France – Bioinformatics & big data
Natacha ROCHEL-GUIBERTEAU, ORCID ID: 0000-0002-3573-5889, Institut de Génétique et de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Strasbourg, France – Structural biology of nuclear hormone receptors
Verdon TAYLOR, ORCID ID 0000-0003-3497-5976, University of Basel, Department of Biomedicine, Basel, Switzerland – Neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases, human iPSCs
Alain WAGNER, ORCID ID: 0000-0003-3125-601X, University of Strasbourg, Laboratory of Design and Application of Bioactive Molecules, Strasbourg, France – Design of bioactive molecules, chemical synthesis
Julianne WINKELMAN, ORCID ID: 0000-0003-2667-9691, Helmholtz Zentrum München, Institute of Neurogenomics, Neuherberg, Germany – Clinical and experimental research on neurologic diseases, neurogenetics
Funding and partners
* Current grants & contracts (to W. Krezel) include:
Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR): "MicroXignal" project (W. Krezel, coordinator)
ERA-Net network & grant: "RAinRARE" (Retinoid signaling and rare diseases)
Fondation pour l'aide à la recherche sur la sclérose en plaques (ARSEP)
* Previous grants also included ANR, European (ERA-Net), University of Strasbourg, USIAS (Institut d'études avancées de l'Université de Strasbourg : W. Krezel, "USIAS Fellow"), and Foundations (Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale, Fondation de France, France Parkinson, Cure MCOPS12, etc) contracts
* Various fellowships have been obtained to support our PhD students (Life Sciences Doctoral School, IGBMC PhD program, IMCBio Research Doctoral School, Joint grants with foreign Universities, various Foundations for extension/4th year of PhD studies, etc)
News

Congratulations to Hanna SEMAAN on the acceptance of his thesis!
His work, supervised by Wojciech KREZEL and Christine Schaeffer Reiss, is titled:"Proteomic Study of Mechanisms, Targets, and Potential Treatments of…
Read more
Awards and recognitions
Pascal Dollé was appointed at Institut Universitaire de France (IUF: Promotion Junior 2001); at Ordre National du Mérite ("Chevalier": Promotion 2013); and at Inserm Scientific Council (2017-2022); was awarded a « Molecular Biology Leader Award » by Research.com, ranking him 6th in France (436th worldwide) among Molecular Biologists, considering his full publication track record (https://research.com/scientists-rankings/molecular-biology/fr )
Wojciech Krezel was appointed an USIAS (University of Strasbourg Institute for Advanced Studies) Fellow (2018)
Agnès Bloch-Zupan, Professor at Dental School and former team member, was recipient of the Sciences Prize of the "Académie Rhénane" (2015)
Anna Podlesny, a former PhD student, received a “Diamond Grant” from Poland Ministry of Education (2013)
Resources
“Cure MCOPS12” is a registered nonprofit organization dedicated to improve the lives of children and families affected by the MCOPS12 syndrome, caused by mutations in RAR beta
Most of our scientific publications are in open access (see below, use the "download" link). Two recommended review articles on our research topic:
"Retinoic acid signalling during development", M. Rhinn & P. Dollé journals.biologists.com/dev/article/139/5/843/45469/Retinoic-acid-signalling-during-development
"Alternative Retinoid X Receptor (RXR) ligands", W. Krezel et al. www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0303720719301248
Check our latest publication - a collaboration with the team of Sigolène Meilhac at Institut Pasteur & Imagine (Paris):
Publications
-
2007
-
The oxidizing enzyme CYP26a1 tightly regulates the availability of retinoic acid in the gastrulating mouse embryo to ensure proper head development and vasculogenesis.
- Vanessa Ribes
- Valérie Fraulob
- Martin Petkovich
- Pascal Dollé
Developmental Dynamics ; Volume: 236 ; Page: 644-53
-
Regulation of expression of the retinoic acid metabolizing enzyme CYP26A1 in uteri of ovariectomized mice after treatment with ovarian steroid hormones.
- Britta Fritzsche
- Julien Vermot
- Ulrike Neumann
- Anja Schmidt
- Florian J Schweigert
- Pascal Dollé
- Ralph Rühl
Molecular Reproduction and Development ; Volume: 74 ; Page: 258-64
-
-
2006
-
Rescue of morphogenetic defects and of retinoic acid signaling in retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (Raldh2) mouse mutants by chimerism with wild-type cells.
- Julien Vermot
- Nadia Messaddeq
- Karen Niederreither
- Andrée Dierich
- Pascal Dollé
Differentiation / The Journal of the International Society of Differentiation ; Volume: 74 ; Page: 661-8
-
Retinoic acid signalling is required for specification of pronephric cell fate.
- Jérôme Cartry
- Massimo Nichane
- Vanessa Ribes
- Alexandre Colas
- Jean-Francois Riou
- Tomas Pieler
- Pascal Dollé
- Eric J Bellefroid
- Muriel Umbhauer
Developmental Biology ; Volume: 299 ; Page: 35-51
-
Retinoic acid regulates morphogenesis and patterning of posterior foregut derivatives.
- Zengxin Wang
- Pascal Dollé
- Wellington V Cardoso
- Karen Niederreither
Developmental Biology ; Volume: 297 ; Page: 433-45
-
Dynamic expression of retinoic acid-synthesizing and -metabolizing enzymes in the developing mouse inner ear.
- Raymond Romand
- Takako Kondo
- Valérie Fraulob
- Martin Petkovich
- Pascal Dollé
- Eri Hashino
Journal of Comparative Neurology ; Volume: 496 ; Page: 643-54
-
Genetic and pharmacological evidence that a retinoic acid cannot be the RXR-activating ligand in mouse epidermis keratinocytes
- Cécile Calléja
- Nadia Messaddeq
- Benoit Chapellier
- Haiyuan Yang
- Wojciech Krezel
- Mei Li
- Daniel Metzger
- Bénédicte Mascrez
- Kiminori Ohta
- Hiroyuki Kagechika
- Yasuyuki Endo
- Manuel Mark
- Norbert Ghyselinck
- Pierre Chambon
Genes and Development ; Volume: 20 ; Page: 1525-1538
-
Distinct roles for retinoic acid receptors alpha and beta in early lung morphogenesis.
- Tushar J Desai
- Felicia Chen
- Jining Lü
- Jun Qian
- Karen Niederreither
- Pascal Dollé
- Pierre Chambon
- Wellington V Cardoso
Developmental Biology ; Volume: 291 ; Page: 12-24
-
Effects of rexinoids on thyrotrope function and the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis.
- Vibha Sharma
- William R Hays
- William M Wood
- Umarani Pugazhenthi
- Donald L St Germain
- Antonio C Bianco
- Wojciech Krezel
- Pierre Chambon
- Bryan R Haugen
Endocrinology ; Volume: 147 ; Page: 1438-51
-
Conditional (loxP-flanked) allele for the gene encoding the retinoic acid-synthesizing enzyme retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (RALDH2).
- Julien Vermot
- Jean-Marie Garnier
- Andrée Dierich
- Karen Niederreither
- Richard P Harvey
- Pierre Chambon
- Pascal Dollé
Genesis - The Journal of Genetics and Development ; Volume: 44 ; Page: 155-8
-

