Cryo EM studies of the C. elegans ribosome to illuminate structure-function relations of ribosome heterogeneity
Subgroup Leader : Lasse Bohl JENNER
Teams : Molecular Basis for Protein Synthesis by the Ribosome
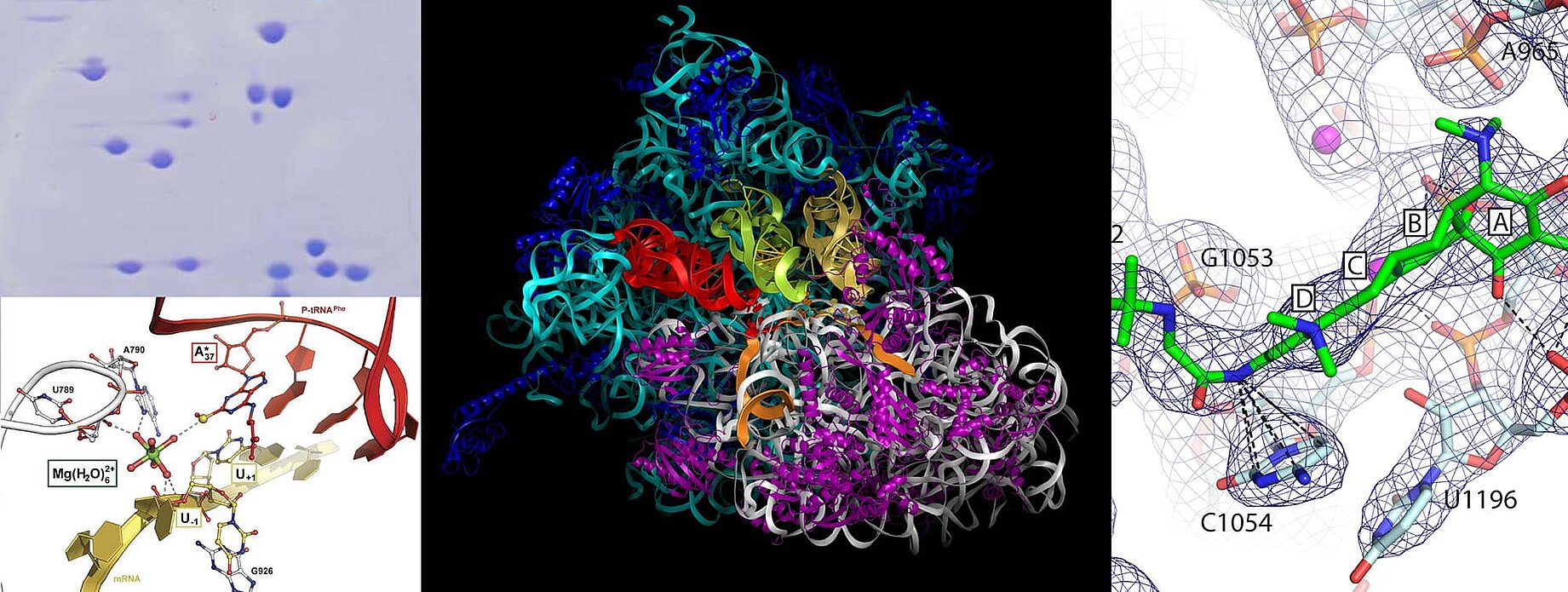
The ribosome is a giant ribonucleoprotein cellular assembly that translates genetic code into protein in all living organisms. Alterations in diverse range of translational machinery cause an extensive and growing catalogue of human diseases. Given the central role of the ribosome in the cell, living organisms have elaborated defense strategies producing chemical substances as for example antibiotics in case of bacteria, to impair ribosome functions in other organism by inhibiting different stages of protein biosynthesis. That is why the ribosome is one of the main antibiotic targets in the cell. More than 40% of clinically useful antibiotics target the ribosome apparatus. Similarly, the eukaryotic ribosome is a major target for small-molecules inhibitors produced as secondary metabolites by bacteria, fungi and plants.
The overall goal of our research is to gain structural insights into the mechanism of protein synthesis by the ribosome, and the mode of action of ribosome-targeting inhibitors. For this, our group are working with both X-ray crystallography as well as cryo Electron Microscopy. We have developed methods for studying the bacterial 70S ribosome from the extreme thermophilic microorganism Thermus thermophilus as well as for the 80S ribosome from the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans, which we trap at different steps of protein biosynthesis or in complex with inhibitors/antibiotics and determine their structures.

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/e/2/csm_AS_2024_originale_defloutee_26f15c5566.jpg)
This award aims to highlight young researchers, who are the first authors of published articles, by offering them the opportunity to be presented by…
Read more